What is wrapped Ethereum (wETH) and how does it work?
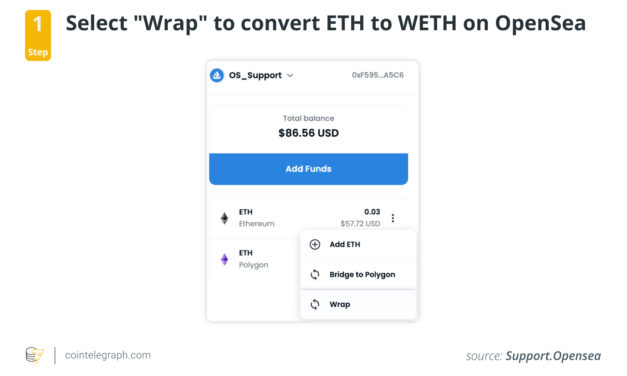
Traders who use the Ethereum network are familiar with the ERC-20 technical standard and have most likely traded and invested in tokens that utilize it. After all, its practicality, transparency and flexibility have made it the industry norm for Ethereum-based projects.As such, many decentralized applications (DApps), crypto wallets and exchanges natively support ERC-20 tokens. However, there’s one problem: Ether (ETH) and ERC-20 do not exactly follow the same rules, as Ether was created way before ERC-20 was implemented as a technical standard.So, why does wrapped ETH matter? Briefly put, ERC-20 tokens can only be traded with other ERC-20 tokens, not Ether. In order to bridge this gap and enable the exchange of Ether for ERC-20 tokens (and vice versa), the Ethereum network introduced wrapped Ethereum (wETH). That said, wETH is the ERC-20 tradable version of ETH.What is wrapped Ether (wETH)?As mentioned, wETH is the wrapped version of Ether, and it’s named as such because wETH is essentially Ether “wrapped” with ERC-20 token standards. Wrapped coins and tokens virtually have the same value as their underlying assets. So, is wrapped Ethereum safe to trade and invest in? The answer is yes, as far as Ethereum is concerned. wETH is pegged to the price of ETH at a 1:1 ratio, so they’re basically the same. The only difference between wrapped tokens and their underlying assets is their use cases, especially for older coins like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ether.Wrapped tokens are like stablecoins, to a certain degree. Come to think of it, stablecoins can also be considered “wrapped USD,” since they have the same value as their underlying asset, the United States dollar. They can also be redeemed for fiat currencies at any time.Bitcoin also has a wrapped version called Wrapped Bitcoin, which has the same value as Bitcoin. The same goes for other blockchains like Fantom and Avalanche.Wrapped Ethereum tokens can be unwrapped after they’ve been wrapped, and the process is simple: Users just have to send their wETH tokens to a smart contract on the Ethereum network, which will then return an equal amount of ETH. Wrapped tokens solve interoperability issues that most blockchains have and allow for the easy exchange of one token for another. For example, users cannot normally utilize Ether on the Bitcoin blockchain or Avalanche on the Ethereum blockchain. Through wrapping, underlying coins are tokenized and wrapped with a certain blockchain’s token standards, thus allowing for their use on that network.How does wrapped Ethereum (wETH) work?Unlike Ether, wETH cannot be used to pay gas fees on the network. Because it is ERC-20 compatible, however, it can be used to provide more investment and staking opportunities on DApps. wETH can also be used on platforms like OpenSea to buy and sell through auctions.Wrapping Ether tokens involves sending ETH to a smart contract. The smart contract will generate wETH in return. Meanwhile, ETH is locked to ensure that the wETH is backed by a reserve. Whenever wETH is exchanged back into ETH, the exchanged wETH is burned or removed from circulation. This is done to ensure that wETH remains pegged to the value of ETH at all times. wETH can also be acquired by swapping other tokens for it on a crypto exchange, such as SushiSwap or Uniswap.So, what is the point of wrapped Ethereum? According to WETH.io, the ultimate goal is to update Ethereum’s codebase and make it ERC-20 compliant in itself, eventually eliminating the need to wrap Ether for the purpose of interoperability. But, until then, wETH continues to remain useful in providing liquidity to liquidity pools, as well as for crypto lending and NFT trading, among others. In short, it’s not really a matter of ETH vs. wETH since wrapping Ethereum is more of a workaround than a permanent solution. With the number of upgrades slated to happen on the Ethereum network over the years, Ethereum seems to be moving closer toward better interoperability by the day.How to wrap Ether (ETH)?There are several ways to wrap Ether. As mentioned, one of the most common ways to do so is by sending ETH to a smart contract. Another method is swapping wETH for another token via a crypto exchange.Let’s look at three ways to generate wETH in the sections below:Using the wETH smart contract on OpenSeaIn this example, we’ll be using the OpenSea platform to convert ETH to wETH using the wETH smart contract.First, click on “Wallet,” located at the top-right corner of OpenSea. Then, click on the three dots next to Ethereum and select “Wrap.”Next, enter the value for the amount of ETH to be converted to wETH. Then, click “Wrap ETH.” This will call the wETH smart contract to convert ETH into wETH.A MetaMask pop-up will appear, prompting the user to sign the transaction. A confirmation message will then appear once the wrap is complete.The converted wETH will show up in the wallet portion of the user’s OpenSea account. The wETH will bear a pink Ethereum diamond as its logo, distinguishing it from ETH.Generating wETH via UniswapWhen using Uniswap, a user first has to connect their wallet and ensure the Ethereum network is selected.Then, click “Select Token,” located at the bottom field, and select wETH from the list of options. Now, input the amount of ETH to be converted to wETH and click “Wrap.”The transaction will then need to be confirmed from the user’s crypto wallet. Gas fees in ETH will also need to be paid at this stage. Once all the details are in order and the transaction has been confirmed from the user’s end, all that’s left to do is to wait for the transaction to be confirmed in the blockchain.Generating wETH with MetaMaskUpon opening the MetaMask wallet, begin by ensuring that the selected network is “Ethereum Mainnet.” Then, click “Swap.”Then, select wETH from the “Swap to” field.Next, input the amount of ETH to be swapped. Then, click “Review Swap.”A window displaying a quote of the conversion rate will appear. Since it involves the conversion of ETH to wETH, the rate should be 1:1. To finalize the transaction, click “Swap.”How to unwrap Ether (ETH)?Unwrapping Ether can also be done manually, such as by interacting with a smart contract. For instance, ETH can also be unwrapped in the same way that it can be wrapped via the wETH smart contract on OpenSea. The only difference is that instead of clicking “Wrap ETH,” the user has to click “Unwrap wETH.”The same goes for swapping wETH back to ETH, which can be done by using Uniswap or MetaMask. The process for unwrapping is essentially the same as the process outlined above for wrapping ETH on both platforms. The only difference is that the values should be changed (from wETH to ETH).What are the risks of using wrapped tokens?Ethereum co-creator Vitalik Buterin himself pinpointed one of the main disadvantages of wrapped assets. According to Buterin, the main problem with many of these wrapped assets is their sensitivity to centralization. Currently, wrapping assets are not Turing-complete and cannot be automated via the Ethereum blockchain. As discussed, wrapping is usually only carried out using central programs, thus the concern for possible manipulation and abuse.Issued wrapped tokens depend on the third-party platforms that issue them, inevitably subjecting decisions pertaining to wrapped assets to central entities. Buterin voiced his concerns about the possibility of such a mechanism undermining the core principles of decentralization and transparency that the blockchain industry stands for.Future of wrapped tokensCurrently, wrapped tokens make it possible for blockchains to interact with one another. This allows for a much more decentralized ecosystem, where tokens can be easily traded or exchanged between different platforms.Better interoperability solutions are on the horizon, such as updating blockchains’ codebases to be compatible with each other or using bridge chains. For Ethereum, at least, the plan is to eventually phase out the use of wrapped tokens like wETH alongside network developments.This does not mean that wrapped tokens are going away anytime soon. They will continue to play an important role, providing valuable service to those who need it. For one, wrapped tokens can serve as a stabilizing force between different blockchains, as they help maintain consistent prices between them.They can also help facilitate cross-chain atomic swaps, which are becoming increasingly popular. In the long run, however, wrapped tokens will likely become less and less necessary as blockchains become more interoperable.Purchase a licence for this article. Powered by SharpShark
Čítaj viac